25/08/2023
25/08/2023
Mr. Mrityunjay Ojha
5 Mins to Read
Table of content
What is Migration Lag in SEO?
In the ever-evolving landscape of the digital world, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role in determining a website’s visibility and success. As businesses and websites undergo transformations – be it a complete redesign, migration to a new domain, or structural changes – a phenomenon known as “migration lag” can significantly impact their SEO performance.
In this blog, we’ll delve into what migration lag in SEO is, why it occurs, and how to effectively manage it to ensure a seamless transition without sacrificing search rankings
What is Migration Lag?
Migration lag refers to the period during which a website’s search rankings and visibility experience a temporary decline after undergoing significant changes or migrations. This phenomenon arises due to the time it takes for search engines to fully process and index the alterations made to a website.
During this period, a website might not appear as prominently in search engine results pages (SERPs) as it did prior to the changes. This lag can range from a few days to several weeks, depending on various factors.
Factors Influencing Migration Lag SEO
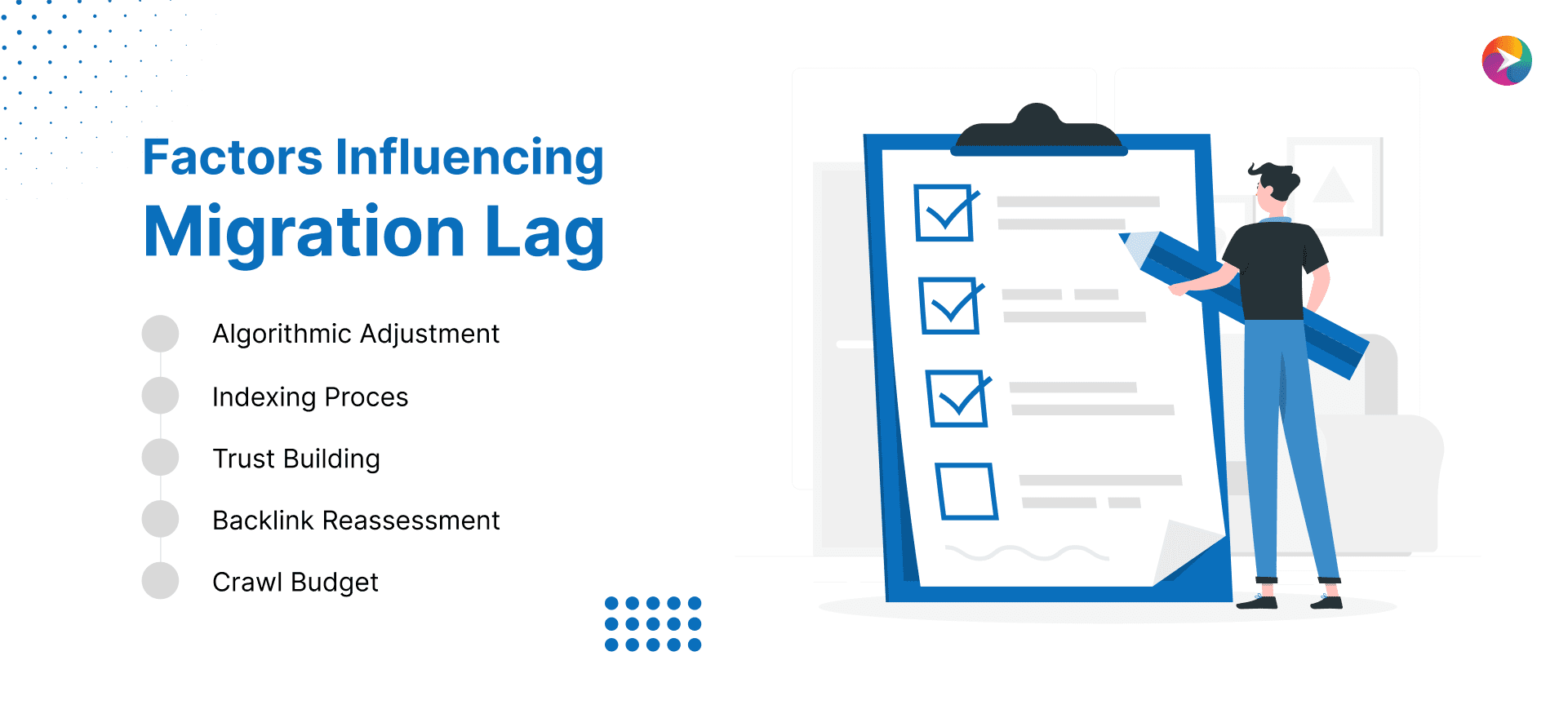
Several factors contribute to the occurrence and duration of migration lag in SEO:
1. Algorithmic Adjustment: Search engines, particularly Google, utilize complex algorithms to assess and rank websites. When substantial changes occur, such as domain migrations or significant content modifications, these algorithms need time to reassess and determine the website’s new position in search results.
2. Indexing Process: Search engines continually crawl and index websites to update their databases. However, during times of significant changes, the indexing process might take longer due to the increased complexity of evaluating new content, structure, and interlinking.
3. Trust Building: For new domain migrations, search engines need time to build trust and authority for the new domain. This involves analyzing the website’s consistency, quality, and user experience over a period before reinstating its previous search rankings.
4. Backlink Reassessment: Changes in a website’s structure or content might lead to a reassessment of its backlink profile. This can affect the website’s authority and, subsequently, its search rankings.
5. Crawl Budget: Search engines allocate a specific crawl budget to each website, determining how often they crawl and index its pages. During migration lag, this budget might be temporarily affected as search engines prioritize crawling and indexing other critical changes across the web.
Managing Migration Lag SEO Effectively
While migration lag is an anticipated consequence of significant website changes, there are steps you can take to minimize its impact on your SEO:
1. Thorough Planning: Before making any major changes, create a comprehensive migration plan that outlines the steps, potential risks, and contingencies. This includes creating 301 redirects for old URLs to new ones, ensuring proper HTML sitemaps, and implementing structured data markup.
2. Monitor Performance: Keep a close eye on your website’s analytics and search performance before, during, and after the migration. Monitoring performance metrics can help you identify any negative trends early on and take corrective measures.
3. Maintain Consistency: While making changes, strive to maintain consistency in your content, branding, and messaging. This reduces confusion for both users and search engines and expedites the trust-building process.
4. Test Rigorously: Before the actual migration, thoroughly test the new website or changes on a staging environment. This allows you to identify and rectify any technical issues that could negatively impact SEO.
5. Update Internal Links: Ensure that all internal links are updated to point to the new URLs. Broken or outdated links can hinder search engines’ ability to crawl and index your content efficiently.
6. Patience is Key: Recognize that migration lag is a natural part of the process. Avoid making further changes or panicking during this period, as it could disrupt the algorithms’ assessment and potentially prolong the lag.
7. Crawl Budget: Search engines allocate a specific crawl budget to each website, determining how often they crawl and index its pages. During migration lag, this budget might be temporarily affected as search engines prioritize crawling and indexing other critical changes across the web.
Final Thoughts
Migration lag in SEO is a temporary setback that many websites experience when undergoing significant changes. While it might cause a dip in search rankings and visibility, proper planning, meticulous execution, and patience can mitigate its impact. Remember that SEO is a long-term strategy, and the short-term fluctuations during migration lag can lead to long-term gains if managed effectively.
By understanding the factors at play and following best practices, you can ensure a smoother transition and maintain your website’s search visibility in the ever-competitive digital landscape.

 Mobile Apps
Mobile Apps Web Apps
Web Apps Blockchain
Blockchain Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing Others
Others